Retained Earnings: Calculation, Management, and Uses Explained

This process prepares accounts for the next financial year, allowing the business to start fresh with zero balances in its income and expense accounts. The normal balance of retained earnings is a credit balance. This means that retained earnings typically increase with credits and decrease with debits.
Types of Accounts
This rule is the inverse of the rule for asset accounts, which increase with a debit and decrease with a credit. Since Retained Earnings increases when a company earns income, and that income is a source of equity, the account naturally carries a credit balance. In contrast, a permanent account is a balance sheet account. It is permanent because it is not closed at the end of each accounting period. At the start of the new accounting period, the closing balance from the previous accounting period is brought forward and becomes the new opening balance on the account. Other than the retained earnings account, closing journal entries do not affect permanent accounts.
The Role of Debits and Credits in Bookkeeping
- These temporary accounts are closed to determine the net profit or loss.
- Appropriated retained earnings are those set aside for specific purposes, such as funding capital expenditures or paying off debt.
- Imagine a reservoir of funds, steadily growing with each fiscal period, held back by a company for future investment, debt reduction, or as a cushion against unforeseen financial challenges.
- Yes, having high retained earnings is considered a positive sign for a company’s financial performance.
- Typically, this cash is repaid through investment in work capital, fixed investment investments, or for repayment.
- Calculating retained earnings is a pretty straightforward process.
Prior period adjustments directly affect retained earnings. These adjustments correct errors in previously issued financial statements. When an error is discovered, it is corrected by adjusting the beginning retained earnings balance in the earliest period presented in the financial statements. This ensures that the financial statements are accurate and reliable. Generally, companies like to have positive net income and positive retained earnings, but this isn’t a hard-and-fast rule.
How Debits and Credits Affect Different Account Types
There are plenty of options out there, including QuickBooks, Xero, and FreshBooks. First, revenue refers to the total amount of money generated by a company. It is a key indicator of a company’s ability to generate sales and it’s reported before deducting any expenses. Shareholders, analysts and potential investors use the statement to assess a company’s profitability and dividend payout potential. Retained earnings are reported in the shareholders‘ equity section of a balance sheet. An optional dividend is one where shareholders can choose between cash, stock, or a combination of both.


Debit simply means on the left side of the equation, whereas credit means on the right hand side of the equation as summarized in the table below. Owner distribution is the allocation of the company retained earnings to the owners. Try Wafeq, the advanced electronic accounting and invoicing system, and join the thousands of business owners who use our integrated system. Retained earnings are calculated only when company obligations include dividend payouts. Retained earnings are the percentages of a business’s profits that can be retained but are reinvested in the business instead. Retained earnings can retained earnings debit or credit also be used to pay down debt or increase reserves.
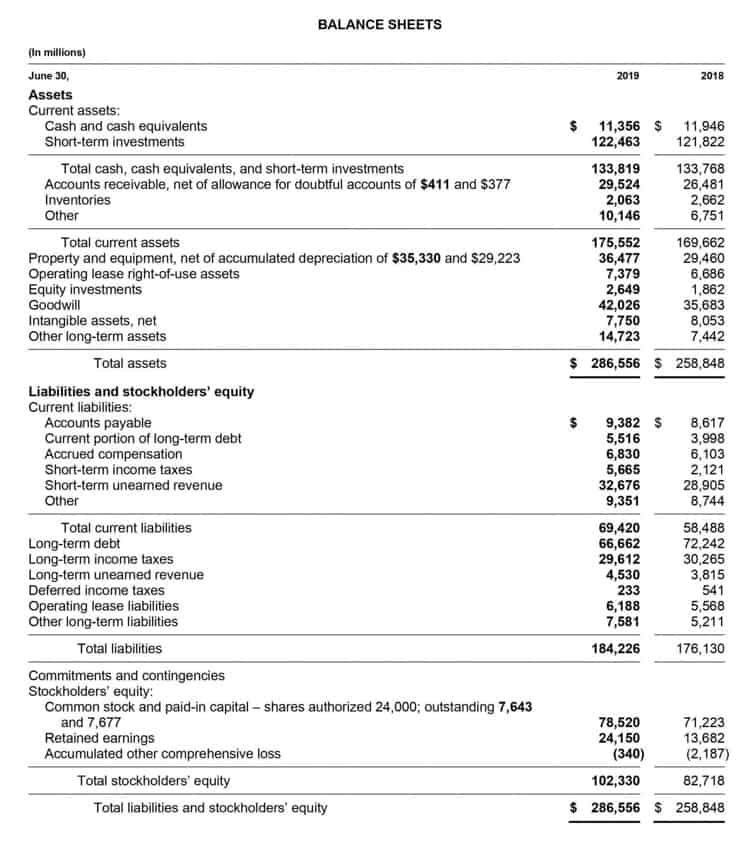
They are typically found in the equity section, which is located at the bottom half of the balance sheet. Net income and retained earnings may have distinctive differences, but both play a pivotal role in allowing financial professionals to gain a better look at their company’s finances. This financial flexibility adds resilience to the business, helping it navigate harsh market conditions.

This, of course, depends on whether the company has been pursuing profitable growth opportunities. Retained earnings are the cumulative net earnings or profits a company keeps after paying dividends to shareholders. Dividends are the last financial obligations paid by a company during a period. “Retained” refers to the fact that those earnings were kept by the company. If the company realizes Net Income, a final credit entry is made directly to the permanent Retained Earnings account.

- Retained earnings can also be credited with the net profit earned during the current period.
- You’ll find retained earnings on the balance sheet, tucked into the stockholder’s equity section.
- Either way, dividends are an important way for shareholders to generate income from their investment in a corporation.
- When losses surpass profits, a debit balance, also known as an “accumulated deficit,” occurs.
They can be used to track a company’s progress over time or to compare HOA Accounting it to other businesses. A financial statement is an important tool for business owners and investors. Calculating ending retained earnings involves adding the net income (or subtracting the net loss) for the period to the beginning retained earnings and then subtracting any dividends paid.
- While retained earnings are reduced, the paid-in capital account (another equity account) is increased by the same amount, resulting in no net change in total equity.
- This heading should identify the company’s name, the document’s title as “Statement of Retained Earnings,” and the specific time frame the statement covers, typically one accounting period.
- Yes, retained earnings can turn negative if a company consistently loses money or pays out more in dividends than it earns.
- The company decided to retain the earnings for that year and utilize them for further growth.
- We’ll explain everything you need to know about retained earnings, including how to create retained earnings statements quickly and easily with accounting software.
- This financial flexibility adds resilience to the business, helping it navigate harsh market conditions.
In accounting, the company usually makes the journal entry for retained earnings when it makes the closing entry after transferring net income or net loss to the income summary account. However, the company may also make the journal entry that includes the retained earnings account when it needs to make the prior period adjustment. The balance of Retained Earnings changes through the application of year-end closing entries, bookkeeping which transfer the balances of temporary accounts. Revenue accounts normally carry a credit balance, while expense accounts normally carry a debit balance.